Basic Networking Topology
This article describes common topologies used for networking. These are a very basic examples, and large networks often use a combination of two or more topologies.
Introduction
The term "topology" is used to describe the infrastructure of a network. It is a basic map or scheme of how the network is constructed. Viewing the topology of a network is a lot like looking at the map of city. You can see the central points or landmarks. Popular points of the cities are usually surrounded by a dense population of residents. The same is true for computer networks. The popular points (usually servers) are surrounded by residents (client machines) that connect to the server.If you read a networking book about topology, they will probably cover the physical types of topologies like star, ring, bus, and mesh. While these were all commonly used topologies at one point in time, star is the primary topology used today. The others may be used in special circumstances or to connect a large group of routers. For example, the Internet backbones use a combination of ring and mesh topologies for a self-healing and reliable network.
Within a LAN, there are two main types of structures used within topologies. Server-based networks are the most common among businesses and large organizations. Peer-to-Peer (p2p) are popular among Internet networks and file sharing services. The tables below outline the pro's and con's of each.
Server-Based Networks
| Pro's | Con's |
|---|---|
| Easily managed security policy | Files are not accessible if the server goes down |
| Files are centrally located | Hackers target the server as a central point to gain full access of a network |
| Files are easy to backup | Network servers can be expensive |
The idea of this is to store files on a server. All other machines (clients) on a network access files from the server. Using a server-based network is also used because it is an efficient way to offer other services to clients such as firewall protection, DHCP, etc. For more information on servers see network and Internet servers.
Peer-to-Peer Networks
| Pro's | Con's |
|---|---|
| No server needed, equipment is cheap | Security Policy can be hard to control |
| Network traffic is distributed among clients | Backup is challenging |
| Files are scattered across different machines |
Topology Structures
The diagrams below show star, ring, and mesh topologies. I will not cover bus topology because it is VERY rarely used. Remember that large networks often use a combination of these topologies depending on certain needs or projects. Peer-to-Peer has become popular among file sharing networks like Edonkey and WinMX. It is also used with BitTorrent.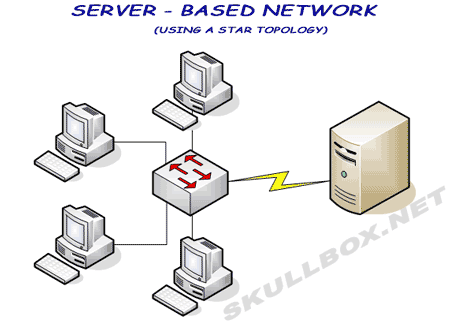
The server-based network using a star topology is the most common. As you can see, the server has a high speed connection to a switch that feeds the client machines. Servers are designed to accommodate high traffic loads from clients. Although it is not shown in the diagram, servers are always protected using a firewall.
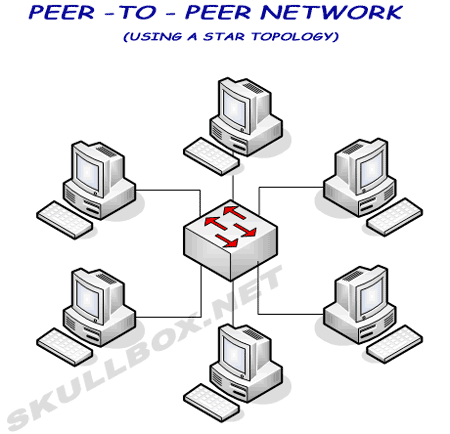
In a peer-to-peer (p2p) network, all files are shared among existing machine. There is no server, so all machines must sustain traffic loads from other clients. Bottle necking and network saturation are common problems among p2p networks. This is often helped with the use of software that offers bandwidth throttling to control the amount of bandwidth in and out of each machine.
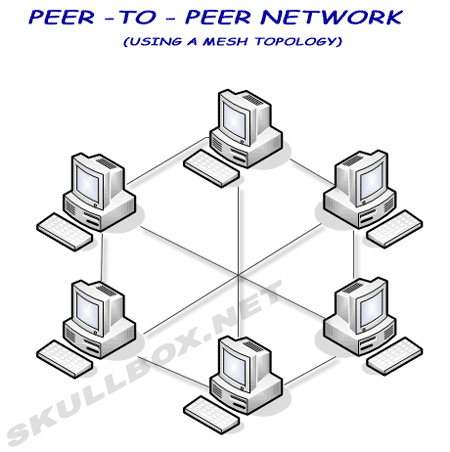
As you can see in the mesh network, each machine has multiple connections with other machines. This is commonly used in large networks connect routers using the BGP protocol. Using a mesh topology increases the uptime of the network because every machine has another path for data if one or even two links goes down. This type of network is expensive and certain devices are not capable of this type of topology.
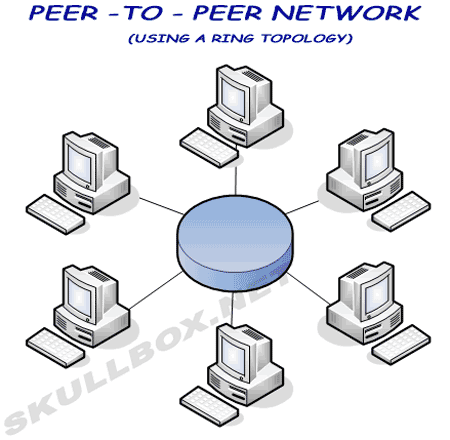
The ring topology is also commonly used to connect routers. Unlike the star, mesh, or p2p networks data is sent around the ring in a "round-robin" fashion. Rings can be configured in several different modes. While some rings only provide 1 physical wire connecting all machines, other rings can be configured with multiple wires to provide alternate paths in the event one wire goes down. This is called "self-healing" and is used in SONET networks.
Comments
Post a Comment